Supertubes offers multiple disaster recovery methods for Apache Kafka.
This section describes how to configure MirrorMaker2 with Supertubes to back up a Kafka cluster to a remote Kafka cluster running on a separate Kubernetes cluster, and how to recover the lost Kafka cluster. This disaster recovery solution uses a MirrorMaker2 active/active, active/passive topology setup.
Note: Supertubes and MirrorMaker2 supports other scenarios as well, such as fan-out, aggregation, or cluster migration. If you want to use Supertubes in one of these scenarios, contact us for details.
How it works 🔗︎
MirrorMaker2 uses the Connect framework to replicate topics between Kafka clusters.
- Both topics and consumer groups are replicated
- Topic configuration and ACLs are replicated
- Cross-cluster offsets are synchronized
- Partitioning is preserved
Supertubes is using MirrorMaker2 to set up cross-cluster replication between remote Kafka clusters and recover a lost Kafka cluster from a remote Kafka cluster. It deploys a MirrorMaker2 instance for each Kafka cluster into the same namespace where the Kafka cluster resides. The MirrorMaker2 instance acts as a:
- Producer targeting the Kafka cluster running on the same Kubernetes cluster and namespace (it is recommended to have MirrorMaker2 deployed close to the target Kafka cluster)
- Consumer for the remote Kafka clusters
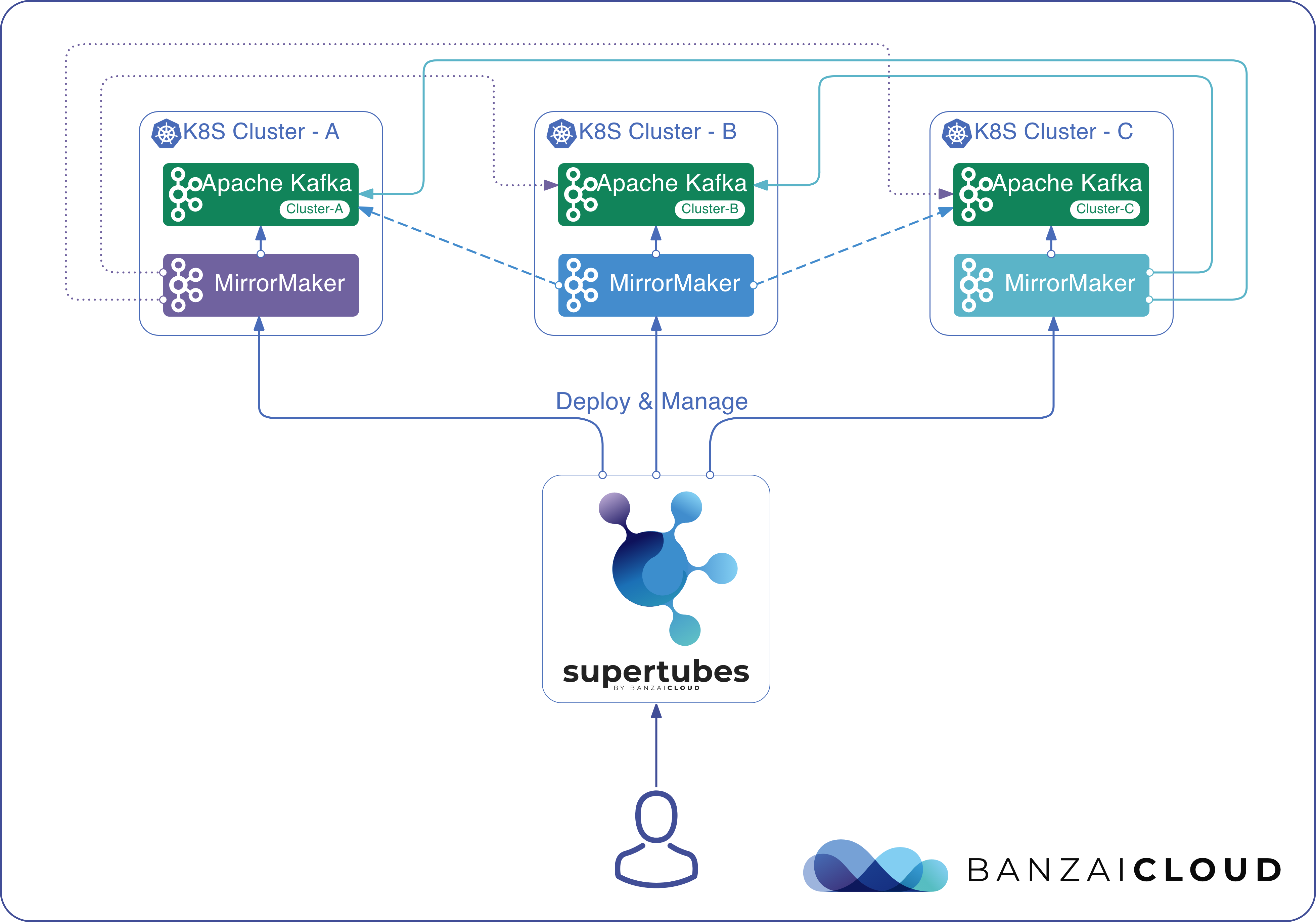
Prepare the MirrorMaker2 descriptor 🔗︎
Supertubes expects a descriptor file in yaml or json format that describes the topology of the Kafka clusters and the MirrorMaker2 replication topology in the following format.
# list of Kubernetes config file paths of clusters hosting our Kafka clusters that we want to make MM2 deployments aware of
kubernetesConfigs:
- # path-to-the-kubeconfig
- # path-to-the-kubeconfig
…
# list of Kafka clusters to make MM2 deployments aware of
kafkaClusters:
- namespace: # kubernetes namespace hosting the Kafka cluster, defaults to 'kafka'
name: # Kafka cluster name, defaults to 'kafka'
kubernetesConfigContext: # name of Kubernetes configuration context as defined in the kubeconfig files which references the Kubernetes cluster hosting the Kafka cluster. If not specified, the default context is used.
alias: # kafka cluster alias by which MM2 refers to this Kafka cluster as (e.g. kafka1). If not provided it defaults to '${kubernetesConfigContext}_${namespace}_${name}'
internalListenerName: # name of the internal listener which local MM2 instances access this Kafka cluster through
externalListenerName: # name of the external listener which remote MM2 instances access this Kafka cluster through
mirrorMaker2Spec:
kafkaHeapOpts: # heap opts setting for MirrorMaker2, defaults to -Xms256M -Xmx2G
resources:
nodeSelector:
tolerations:
affinity:
mirrorMaker2Properties: |
# replication topologies and flows, mm2 config, etc.
# two way replication between 3 Kafka clusters
kafka1->kafka2.enabled=true
kafka1->kafka3.enabled=true
kafka2->kafka1.enabled=true
kafka2->kafka3.enabled=true
kafka3->kafka1.enabled=true
kafka3->kafka2.enabled=true
Supertubes automatically generates the MirrorMaker2 configuration for each MirrorMaker2 instance (MirrorMaker2 has its proprietary configuration format). Supertubes maintains the Kafka servers section of the file, while the replication flows and other MirrorMaker2 settings are populated from the mirrorMaker2Properties provided by the user. The generated MirrorMaker2 configuration file looks like:
# maintained by supertubes
clusters: kafka1, kafka2, kafka3, ...
kafka1.bootstrap.servers=... # internal kafka bootstrap servers URL if MM2 is on the same Kubernetes cluster as Kafka cluster, otherwise external kafka bootstrap servers URL
kafka2.bootstrap.servers=... # internal kafka bootstrap servers URL if MM2 is on the same Kubernetes cluster as Kafka cluster, otherwise external kafka bootstrap servers URL
kafka3.bootstrap.servers=... # internal kafka bootstrap servers URL if MM2 is on the same Kubernetes cluster as Kafka cluster, otherwise external kafka bootstrap servers URL
# user provided mm2 settings
kafka1->kafka2.enabled=true
kafka1->kafka3.enabled=true
kafka2->kafka1.enabled=true
kafka2->kafka3.enabled=true
kafka3->kafka1.enabled=true
kafka3->kafka2.enabled=true
Note: Keep the replication flow settings the same across all MirrorMaker2 instances to avoid omitting topics from cross-cluster replication.
In the example above, MirrorMaker2 will replicate topics from kafka1 to kafka2 and the other way around:
- topics from kafka1 are replicated to kafka2 as kafka1.{topic-name}, similarly
- topics from kafka2 are replicated to kafka1 as kafka2.{topic-name}.
As an example, if we have a topic named topic1 on both Kafka clusters, then:
- kafka1 will have topic1 and kafka2.topic1, and
- kafka2 will have topic1 and kafka2.topic1, respectively.
Bidirectional cross-cluster replication happens similarly between kafka2 <-> kafka3 and kafka1 <-> kafka3.
supertubes mm2 deploy -f <path-to-mm2-deployment-descriptor>
Configure Supertubes and MirrorMaker2 🔗︎
-
Create two Kubernetes clusters, for example, named as
example-k8s-cluster-1andexample-k8s-cluster-2. -
Install Supertubes on both Kubernetes clusters.
-
Provide a common root certificate for the Istio deployments. To ensure that the Kafka clusters are accessed through TLS, Supertubes automatically sets up an Istio service mesh, and runs Kafka inside the mesh on each Kubernetes cluster. That way, Istio handles TLS at the networking layer.
supertubes install --root-cert=root-cert.pem --ca-cert=ca-cert.pem --ca-key=ca-key.pem -a --no-demo-cluster -c {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml}If you don’t have root and intermediate CA certificates at hand, you can use this tool to generate self-signed certificates quickly.
-
Repeat the previous step for the other cluster.
-
-
Create Kafka clusters on both Kubernetes clusters
supertubes cluster create --namespace kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/banzaicloud/koperator/master/config/samples/kafkacluster-with-istio.yamlsupertubes cluster create --namespace kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml} -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/banzaicloud/koperator/master/config/samples/kafkacluster-with-istio.yaml -
Wait until the Kafka clusters becomes operational:
supertubes cluster get --namespace kafka --kafka-cluster kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} Namespace Name State Image Alerts Cruise Control Topic Status Rolling Upgrade Errors Rolling Upgrade Last Success kafka kafka ClusterRunning banzaicloud/kafka:2.13-2.4.0 0 CruiseControlTopicReady 0 2020-03-04 14:07:36 -
Enable cross-cluster replication with MirrorMaker2. In the MirrorMaker2 descriptor file, you have to reference the Kafka clusters. For example, the one running on example-k8s-cluster-1 as kafka1 and the one running on example-k8s-cluster-2 as kafka2.
supertubes mm2 deploy -f -<<EOF # list of Kubernetes config file paths of clusters hosting our Kafka clusters that we want to make MM2 deployments aware of kubernetesConfigs: - {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} - {example-k8s-cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml} # list of Kafka clusters to make MM2 deployments aware of kafkaClusters: - namespace: kafka name: kafka kubernetesConfigContext: kubernetes-admin@example-k8s-cluster-1 # the context from {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} alias: kafka1 # name MM2 refers to this Kafka cluster to internalListenerName: internal # name of the Kafka cluster internal listener local MM2 instance to use externalListenerName: external # name of the Kafka cluster external listener remote MM2 instances to use - namespace: kafka name: kafka kubernetesConfigContext: kubernetes-admin@example-k8s-cluster-2 # the context from {example-k8s-cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml} alias: kafka2 # name MM2 refers to this Kafka cluster to internalListenerName: internal # name of the Kafka cluster internal listener local MM2 instance to use externalListenerName: external # name of the Kafka cluster external listener remote MM2 instances to use mirrorMaker2Properties: |- # replication topologies and flows, mm2 config, etc. kafka1->kafka2.enabled=true kafka2->kafka1.enabled=true # we don't have ACLs set so skip replicating them sync.topic.acls.enabled=false EOF -
Create some Kafka topics.
-
Create a topic named testtopic on both Kafka clusters, for example:
supertubes cluster topic create --namespace kafka --kafka-cluster kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} -f -<<EOF apiVersion: kafka.banzaicloud.io/v1alpha1 kind: KafkaTopic metadata: name: testtopic spec: name: testtopic partitions: 3 replicationFactor: 2 config: "retention.ms": "28800000" "cleanup.policy": "delete" EOF -
Repeat the previous step on the other Kafka cluster.
-
-
Generate client certificates. The Kafka clusters run inside an Istio service mesh with TLS enabled. This means you need a client certificate to write messages to your topic. To get a client certificate, run:
supertubes istio certificate generate-client-certificate -c {example-k8s-cluster-1-kubeconfig.yaml} > cert-data.jsonThe returned JSON contains the following fields in base64-encoded format:
- client-cert.pem: the client certificate
- client-key.pem: the client key
- ca-cert.pem: the CA certificate
- root-cert.pem: the root certificate
- cert-chain.pem: the certificate chain containing root and CA certificate
-
Find the public addresses through which the Kafka cluster is exposed on both Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl get svc -n kafka kafka-meshgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kafka-meshgateway LoadBalancer 10.10.171.247 a7c265ab846c14f8fa082773fee7c0da-2063154997.eu-north-1.elb.amazonaws.com 19090:31645/TCP,19091:32240/TCP,19092:32483/TCP,29092:30681/TCP 61mkubectl get svc -n kafka kafka-meshgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kafka-meshgateway LoadBalancer 10.10.161.160 51.124.19.105 19090:32651/TCP,19091:31402/TCP,19092:30403/TCP,29092:31586/TCP 57m -
Write messages to testtopic on both clusters. Use kafkacat to produce and consume messages from/to our testtopic topic.
kafkacat -b a7c265ab846c14f8fa082773fee7c0da-2063154997.eu-north-1.elb.amazonaws.com:29092 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.ca.location=cert_chain.pem -X ssl.certificate.location=client.pem -X ssl.key.location=client.key -P -t testtopic kafka1: message 1 kafka1: message 2kafkacat -b 51.124.19.105:29092 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.ca.location=cert_chain.pem -X ssl.certificate.location=client.pem -X ssl.key.location=client.key -P -t testtopic kafka2: message 1 kafka2: message 2 -
Check replicated messages. Verify that MirrorMaker replicated messages from testtopic from kafka1 to kafka2 under
kafka2.testtopictopic:kafkacat -b a7c265ab846c14f8fa082773fee7c0da-2063154997.eu-north-1.elb.amazonaws.com:29092 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.ca.location=cert_chain.pem -X ssl.certificate.location=client.pem -X ssl.key.location=client.key -C -t kafka2.testtopic -c2 kafka2: message 1 kafka2: message 2kafkacat -b 51.124.19.105:29092 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.ca.location=cert_chain.pem -X ssl.certificate.location=client.pem -X ssl.key.location=client.key -C -t kafka1.testtopic -c2 kafka1: message 2 kafka1: message 1The summary of what you are seeing is:
+-- kafka1 | +-- testtopic | +-- kafka1: message 1 | +-- kafka1: message 2 | +-- kafka2.testtopic | +-- kafka2: message 1 | +-- kafka2: message 2 +-- kafka2 | +-- testtopic | +-- kafka2: message 1 | +-- kafka2: message 2 | +-- kafka1.testtopic | +-- kafka1: message 1 | +-- kafka1: message 2
Recover a lost Kafka cluster 🔗︎
In the event of losing one of the Kubernetes clusters that hosts your Kafka cluster, complete the following steps.
-
While the new cluster is provisioned, direct the client applications (consumers and producers) to the remaining Kafka clusters.
-
Create a new Kubernetes cluster, for example, example-k8s-cluster-new.
-
Wait until the new Kubernetes cluster is ready.
-
Install Supertubes on the new cluster.
supertubes install --root-cert=root-cert.pem --ca-cert=ca-cert.pem --ca-key=ca-key.pem -a --no-demo-cluster -c {example-k8s-cluster-new-kubeconfig.yaml} -
Create a new Kafka cluster to replace the lost one. In the following examples and in the MirrorMaker2 descriptor, we will refer to this new Kafka cluster as
kafka1-new.supertubes cluster create --namespace kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-new-kubeconfig.yaml} -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/banzaicloud/koperator/master/config/samples/kafkacluster-with-istio.yaml -
Wait until the Kafka clusters becomes operational
supertubes cluster get --namespace kafka --kafka-cluster kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-new-kubeconfig.yaml} Namespace Name State Image Alerts Cruise Control Topic Status Rolling Upgrade Errors Rolling Upgrade Last Success kafka kafka ClusterRunning banzaicloud/kafka:2.13-2.4.0 0 CruiseControlTopicReady 0 2020-03-04 16:42:34 -
Create a topic named testtopic in the new Kafka cluster.
supertubes cluster topic create --namespace kafka --kafka-cluster kafka -c {example-k8s-cluster-new-kubeconfig.yaml} -f -<<EOF apiVersion: kafka.banzaicloud.io/v1alpha1 kind: KafkaTopic metadata: name: testtopic spec: name: testtopic partitions: 3 replicationFactor: 2 config: "retention.ms": "28800000" "cleanup.policy": "delete" EOF -
Create a new alias for the new Kafka cluster. The new (replacement) Kafka cluster must get a new alias and should not reuse the alias of the lost Kafka cluster, because MirrorMaker2 doesn’t replicate topics that are prefixed with the name of a cluster alias.
-
Update the MirrorMaker2 topology descriptor file to reflect the new Kubernetes cluster and Kafka cluster alias (
kafka1-new) as well.supertubes mm2 deploy -f -<<EOF # list of Kubernetes config file paths of clusters hosting our Kafka clusters that we want to make MM2 deployments aware of kubernetesConfigs: - {example-k8s-cluster-new-kubeconfig.yaml} - {example-k8s-cluster-2-kubeconfig.yaml} # list of Kafka clusters to make MM2 deployments aware of kafkaClusters: - namespace: kafka name: kafka kubernetesConfigContext: kubernetes-admin@example-k8s-cluster-new alias: kafka1-new # name MM2 refers to this Kafka cluster to internalListenerName: internal # name of the Kafka cluster internal listener local MM2 instance to use externalListenerName: external # name of the Kafka cluster external listener remote MM2 instances to use - namespace: kafka name: kafka kubernetesConfigContext: kubernetes-admin@example-k8s-cluster-2 alias: kafka2 # name MM2 refers to this Kafka cluster to internalListenerName: internal # name of the Kafka cluster internal listener local MM2 instance to use externalListenerName: external # name of the Kafka cluster external listener remote MM2 instances to use mirrorMaker2Properties: |- # replication topologies and flows, mm2 config, etc. kafka1-new->kafka2.enabled=true kafka2->kafka1-new.enabled=true sync.topic.acls.enabled=false EOF -
Run the following command with the modified descriptor file:
$ supertubes mm2 deploy -f <path-to-mm2-deployment-descriptor> -
Wait until Supertubes updates all MirrorMaker2 instances.
-
The new Kafka cluster starts catching up from the other clusters.
-
Verify that all messages from the lost
kafka1cluster are replicated from the backupkafka2cluster to the newly createdkafka1-newreplacement Kafka cluster.kubectl get svc -n kafka kafka-meshgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kafka-meshgateway LoadBalancer 10.10.235.122 abee2dfdb54dc485e8449b776a649377-1677360459.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com 19090:30870/TCP,19091:32756/TCP,19092:30961/TCP,29092:31455/TCP 25mkafkacat -b abee2dfdb54dc485e8449b776a649377-1677360459.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com:29092 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.ca.location=cert_chain.pem -X ssl.certificate.location=client.pem -X ssl.key.location=client.key -P -t testtopic kafka1-new: message 1 kafka1-new: message 2












